25 June 2021
The Botanical garden of the University of Padua
The Botanical garden of the University of Padua was founded in 1545 as an “Horto medicinale” for the cultivation of medicinal plants for scientific and educational purposes. Its establishment was requested by Francesco Bonafede, lecturer in medicinal herbs, so that students could observe living therapeutic plants.
Many of the species were introduced into Italy and Europe for the first time through the Botanical garden of Padua, which benefited from the crucial role, estates and commercial trade of the Venetian Republic. It is the oldest university botanical garden in the world and has kept its original location over the centuries, together with many of the characteristics of the sixteenth century structure. Always a place of scientific research, cultural and educational exchange, it was added to the Unesco list of World Heritage Sites in 1997 with the following motivation: “The Botanical garden of Padua is the origin of all botanical gardens in the world, a cradle of science and scientific exchanges, serving as the basis for the understanding of the relationship between nature and culture. It has made a profound contribution to the development of a number of modern scientific disciplines, notably botany, as well as medicine, chemistry, ecology and pharmacy”.
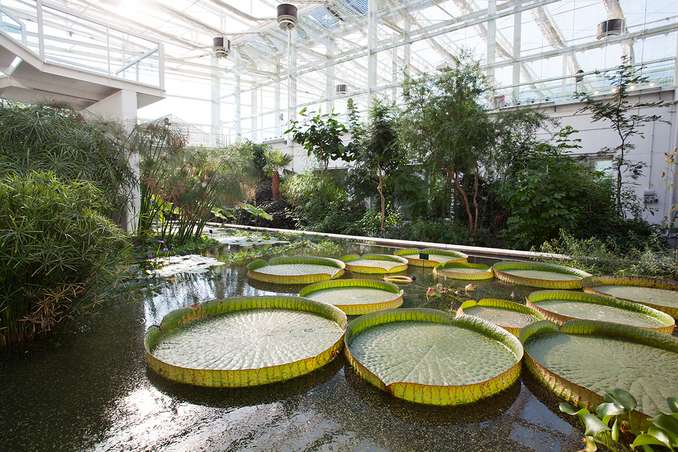
In 2014 the botanical garden extended its plant collection, opening the Biodiversity Garden: five new large glasshouses which offer a journey through five biomes of the Earth whilst interweaving the histories of plants and populations.
Nowadays the Botanical garden of Padua contains over 3500 species with 7000 specimens, including Saint Peter's Palm, planted in 1585 and described by Goethe in his Metamorphosis of Plants, and a rare Platanus orientalis from 1680.
Many of the species were introduced into Italy and Europe for the first time through the Botanical garden of Padua, which benefited from the crucial role, estates and commercial trade of the Venetian Republic. It is the oldest university botanical garden in the world and has kept its original location over the centuries, together with many of the characteristics of the sixteenth century structure. Always a place of scientific research, cultural and educational exchange, it was added to the Unesco list of World Heritage Sites in 1997 with the following motivation: “The Botanical garden of Padua is the origin of all botanical gardens in the world, a cradle of science and scientific exchanges, serving as the basis for the understanding of the relationship between nature and culture. It has made a profound contribution to the development of a number of modern scientific disciplines, notably botany, as well as medicine, chemistry, ecology and pharmacy”.
In 2014 the botanical garden extended its plant collection, opening the Biodiversity Garden: five new large glasshouses which offer a journey through five biomes of the Earth whilst interweaving the histories of plants and populations.
Nowadays the Botanical garden of Padua contains over 3500 species with 7000 specimens, including Saint Peter's Palm, planted in 1585 and described by Goethe in his Metamorphosis of Plants, and a rare Platanus orientalis from 1680.
What is a weed? A weed is a plant whose virtues have not yet been discovered.- Ralph Waldo Emerson - |